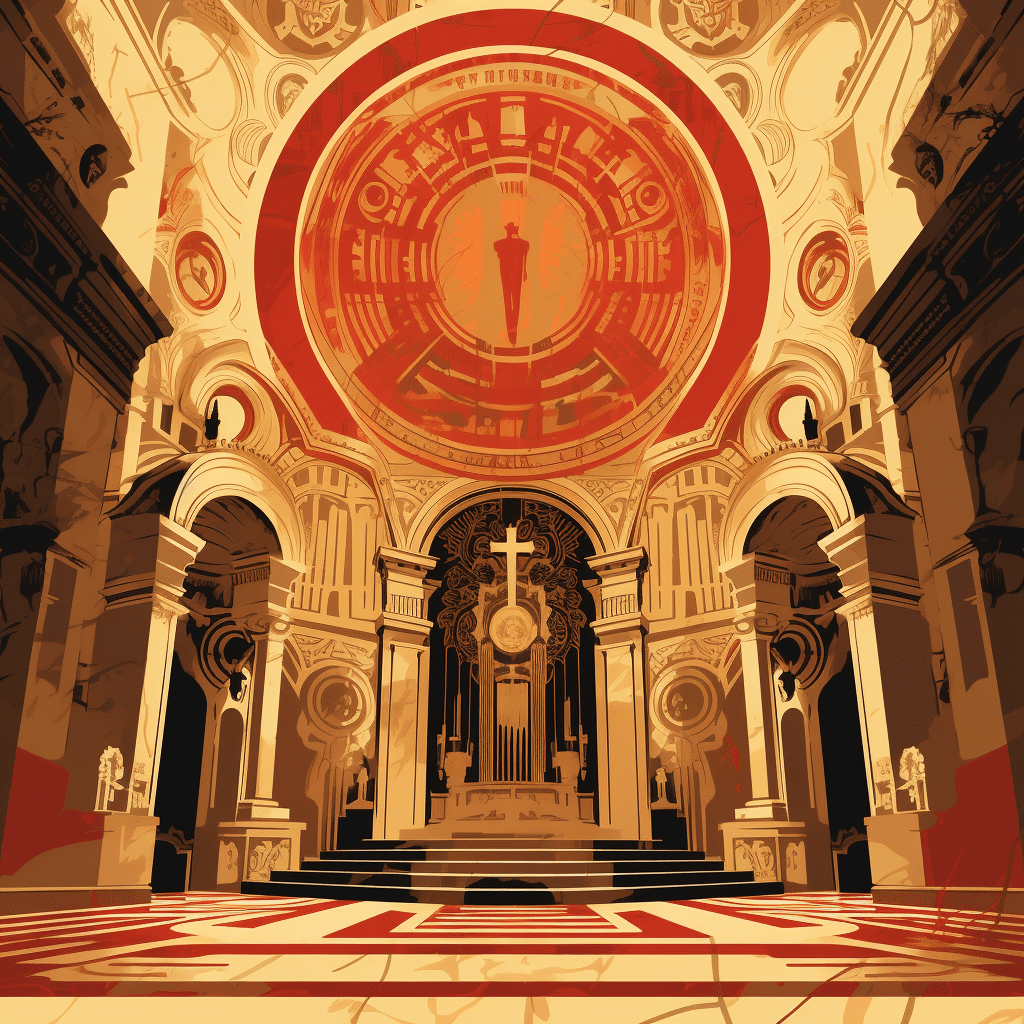
What Is a Basilica?
A basilica is a type of building that has been used for different purposes throughout history. The word “basilica” comes from the Greek word “basiliké,” which means “royal.” In ancient Rome, a basilica was a large public building where people gathered for various activities such as commerce and legal matters. Over time, the term evolved to also refer to a specific architectural style used in Christian churches.
Features of a Basilica
In Christian architecture, a basilica is characterized by a specific set of features. These features include a rectangular shape, with a long central nave (the main aisle) and side aisles. The nave is usually higher and wider than the side aisles, creating a sense of grandeur and emphasizing the central space.
Inside a basilica, you may find columns or piers that separate the nave from the side aisles, providing structural support. These columns or piers often support arches or arcades, adding to the overall aesthetic appeal. At the front of the basilica, there is usually a raised area known as the apse, which is semicircular or polygonal in shape. The apse is where important religious ceremonies take place.
An important visual feature of a basilica is its roof. It often consists of a series of pitched arches, called a gable roof, which provides stability and adds to the architectural charm.
Types of Basilicas
There are various types of basilicas found around the world. The most well-known type is the Papal Basilica, which is located in Rome, Italy. These basilicas are considered major churches and can only be designated as such by the Pope. Saint Peter’s Basilica in Vatican City is an example of a Papal Basilica.
Another type of basilica is the Minor Basilica. These basilicas are also recognized by the Pope but hold a lesser status compared to Papal Basilicas. Saint Patrick’s Basilica in New York City is an example of a Minor Basilica.
Other basilicas may differ in architecture and purpose. For example, some basilicas are built to commemorate significant events or to honor particular saints. These basilicas may attract visitors who come to pray, admire the artwork, or learn about history and religious traditions.
Basilicas in Historical Context
The original concept of a basilica can be traced back to ancient Rome. Roman basilicas were used for various community activities such as business, legal proceedings, and social gatherings. These buildings often had a central hall with aisles, similar to the layout of a Christian basilica.
During the early Christian period, when Christianity was still being persecuted, believers would gather in small, private spaces to worship. However, as the religion gained prominence and became more accepted, Christians sought larger spaces to accommodate larger congregations. They adapted the existing architectural style of Roman basilicas to create Christian places of worship. This allowed them to have a grand, public space for religious gatherings.
The influence of basilicas extended beyond Rome and spread throughout Europe and other parts of the world. Many basilicas reflect the cultural and architectural styles of the regions in which they were built. Some basilicas are adorned with elaborate decorations and artwork, showcasing the creativity and craftsmanship of the time.
Conclusion
In summary, a basilica is a type of building that has its roots in ancient Rome but has evolved to become an important architectural style in Christian churches. It is characterized by a rectangular shape, a central nave, side aisles, and an apse. Basilicas can serve different purposes, ranging from major churches recognized by the Pope to smaller basilicas commemorating historical events or honoring specific saints. They have played a significant role in the development of architectural and religious traditions throughout history.